Previously on our blog posts, we spoke about the benefits of Vitamin A and Vitamin C. Today we will get to know more about Vitamin E.

Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant and a fat-soluble nutrient. As a whole, Vitamin E is classified into tocopherols and tocotrienols, which are organic compounds with Vitamin E activity. Generally, there are eight naturally occurring forms of Vitamin E; namely, the alpha, beta, gamma and delta classes of tocopherol and tocotrienol, which are synthesized by plants. Among the eight natural forms of Vitamin E found in food, alpha-tocopherol is the most active form in the human body. Since Vitamin E is fat-soluble, it is stored in the fatty tissues and liver.
The lack of Vitamin E in the body

Vitamin E deficiency is a very rare condition and is likely to occur due to certain diseases, whereby the fat is not digested or absorbed properly. The deficiency is not due to low dietary intake of Vitamin E. Examples of the diseases include Crohn’s disease, cystic fibriosis and certain rare genetic conditions knows as abetalipoproteinemia and ataxia with Vitamin E deficiency (AVED). AVED is a rare inherited neurodegenerative disorder characterized by impaired ability to coordinate voluntary movements and it also affects the peripheral nervous system. Generally Vitamin E deficiency affects children more easily as compared to adults, as adults have the ability to store Vitamin E in their fatty tissue.
Common symptoms of Vitamin E deficiency include:
- Difficulty with walking and coordination
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Visual disturbances
- General unwellness
Are you taking enough Vitamin E in your diet?
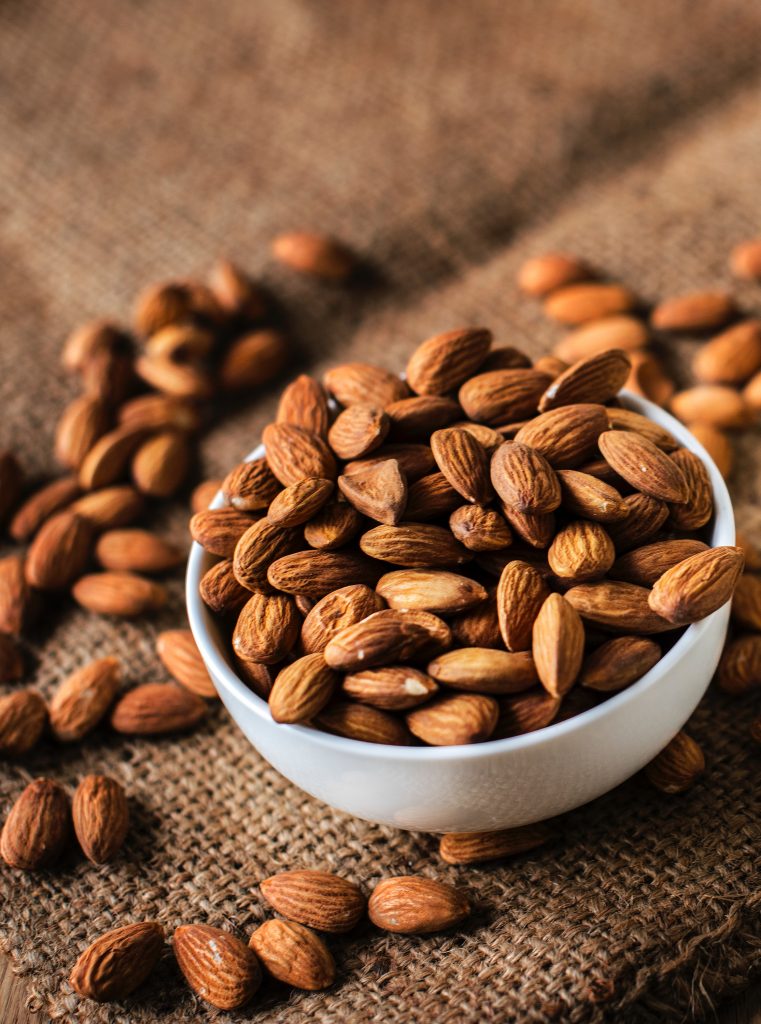

Ever wonder what you should be eating to get your daily dose of Vitamin E? Vitamin E is found in a wide variety of foods and supplements such as:
- Nuts – almonds, sunflower seeds
- Green leafy vegetables – spinach
- Vegetable oils – sunflower oil and safflower oil
- Vitamin E fortified food – milk, grains, bread
Health benefits of Vitamin E
1. Effective anitoxidant.

Antioxidants helps to protect cells from damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals. They are effective in fighting oxidation which can eventually prevent or delay cells from damage and causing chronic diseases.
2. Lower risks of cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin E slows down the formation of plaque in the arteries. In fact, it lowers down the chances of conversion of cholesterol into plaque that clogs the arteries. Plaque consists of cholesterol and other substances found in the blood. The buildup of plaque in arteries can block/reduce the blood flow. Blood supplies oxygen to the cells in our body. Reduced blood flow, will result in cells not receiving enough oxygen and it begins to suffer. When there’s a buildup of plaque in your arteries, you’re at an increased risk for heart attack and stroke.
3. Great looking skin
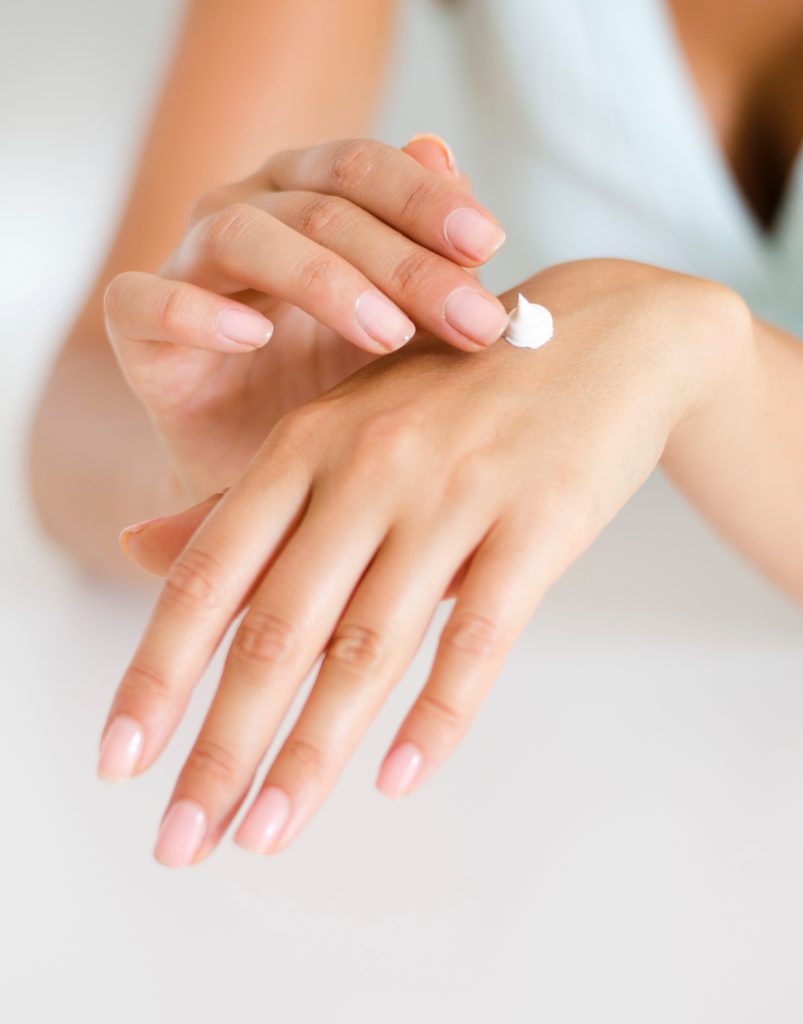

The moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties of Vitamin E plays an important role in your skin health. Moreover, it can also protect your skin against UV damage. This is why you often find Vitamin E as an ingredient in skin care products such as lip balms, serums, lotions, and cleansers.
4. Contributes in brain health.

Free radicals are responsible for the functional decline of the brain in older poeple. Brain damage can happen gradually resulting in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Consumption of Vitamin E rich food is essential for improved cognitive development.
However, bear in mind that Vitamin E is not effective in treating the disease but helps in the prevention of the disease. Comparatively, clinical trials proves that Vitamin E supplements does not help in maintaining cognitive performance or slow its decline. Hence, it is better to skip the pills and consume Vitamin E-rich foods instead.
Get your Vitamin E intake right.

Despite the impressive health benefits of Vitamin E, cooking can reduce the amount of Vitamin E, as they are sensitive to heat and light exposure. Most food containing Vitamin E can be eaten fresh and raw without going through the cooking process. Most of the nuts and seed such as almonds, sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds are eaten raw and are perfect for snacking. Instead of snacking on junk food and processed food, munch on these Vitamin E rich snacks that is good for your body.
What if it is not meant to be consumed raw?
Unless your food containing Vitamin E can only be consumed after cooking, sautéing them in olive oil or other healthy oil is a better option. Drizzling some olive oil on your salad or lightly frying your greens in oil can help you absorb the fat-soluble vitamins contained in vegetables.
Vitamin E can do wonders to your body but keep in mind that everything should be consumed in moderation. Excessive intake of vitamin E can cause toxic build up in the body.
REFERENCES
Traber, M. G., & Manor, D. (2012). Vitamin E. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 3(3), 330-1. doi:10.3945/an.112.002139
Rizvi, S., Raza, S. T., Ahmed, F., Ahmad, A., Abbas, S., & Mahdi, F. (2014). The role of vitamin e in human health and some diseases. Sultan Qaboos University medical journal, 14(2), e157-65.
HENDRICKSON, K. (2019). What Vitamins Clear Away Plaque in the Arteries? | Livestrong.com. [online] LIVESTRONG.COM. Available at: https://www.livestrong.com/article/526291-what-vitamins-clear-away-plaque-in-the-arteries.
Linus Pauling Institute. (2019). Vitamin E and Skin Health. [online] Available at: https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/skin-health/vitamin-E#photoprotection.
Nhan, P. and Hoa, N., 2013. Effect of Light and Storage Time on Vitamin E in Pharmaceutical Products. British Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 4 (5), 176-180.
Whitworth, G. (2018). Vitamin E for Skin. [online] Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/vitamin-e-for-skin [Accessed 28 March. 2019].

