You might be one of the people who runs away whenever you see the word ‘fat’ in any foods. They might have a bad reputation, but they are not useless for us – in fact, we need fat to survive!

Fats have more functions than you think!
1. Source of Energy
Fat is an important source of energy for us.
Its energy content is actually twice of that of carbohydrates and protein!
Fat also functions as an energy reserve in our bodies – when we require more energy due to physical activity or starvation, these energy reserve will come into play.
2. Nutrient absorption
It facilitates the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins – vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E and vitamin K – which are vital for our health. For example, studies suggest that dietary fat is required for the optimal absorption of beta-carotene, an important source of vitamin A in our diet. Vegetable oils are usually high in vitamin E and K. Oily fish is among the few dietary sources of vitamin D.
3. Structural component of cells
Our cells have membranes that separate the inside and outside of the cell. They help us control what are the substances that should enter our cells and what should not. These membranes are mainly made of fats. Therefore, fats are very important in terms of supporting our growth!
4. Provides us with essential fatty acids
You might have not heard of essential fatty acids, but you definitely have come across omega-3 on food packagings in the supermarket!
In fact, essential fatty acids actually refer to the omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids. They are known to be ‘essential’ because they cannot be produced by the human body and must be obtained from our diets.
Apart from supporting our normal growth, they are involved in many important physiological processes such. Blood clotting, wound healing, inflammation any many more – all these depend on essential fatty acids!
5. Protection of internal organs and insulation
Many of the vital organs, especially the kidneys, heart, and intestines are cushioned by fat. This helps protect them from injury and hold them in place.
Besides, fats also insulate the body to preserve body heat and temperature.
How much fat should I consume in a day?
The Malaysian Dietary Guidelines suggest that 25-30% of the total energy intake in adults should be from fats.
This amount would be equivalent to 56 grams to 67 grams of fat of for a person who consumes 2000 kcal per day. Here are also some figures on fat content in foods for your reference:
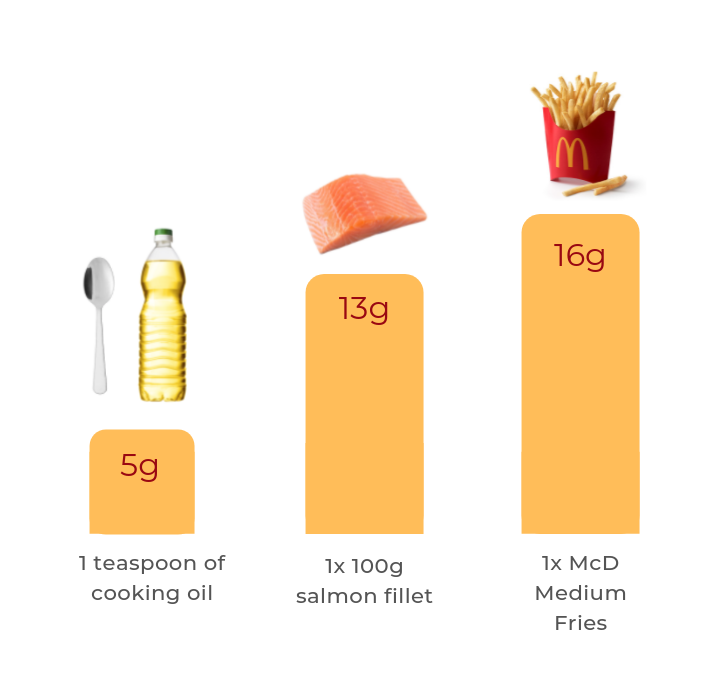
Yes, fats have a wide range of functions in our body, but we should be aware of our fat intake too. This is because when the fat we consume is more than what we need, our bodies store them as adipose tissues.
Excess accumulation of adipose tissues in our bodies would lead to obesity, which is the risk factor for many non-communicable diseases such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, stroke, fatty liver and more.
References
- Green, A. S., & Fascetti, A. J. (2016). Meeting the Vitamin A Requirement: The Efficacy and Importance of β-Carotene in Animal Species. TheScientificWorldJournal, 2016, 7393620. doi:10.1155/2016/7393620
- French Fries | McDonald’s® Malaysia. (2019). [online] Available at: https://www.mcdonalds.com.my/menu/french-fries?gclid=Cj0KCQjwv8nqBRDGARIsAHfR9wCukf7cdLuapftcErBVBBsB8wMprP3_aMPTA_imdYCZq01LhFSQy1saAsqxEALw_wcB [Accessed 14 Aug. 2019].
- Recommended Nutrient Intakes for Malaysia (2019). [online] Available at: http://nutrition.moh.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/FA-Buku-RNI.pdf [Accessed 14 Aug. 2019].

